2025-4-18 16:38:39
2025-4-18 16:38:39 admin
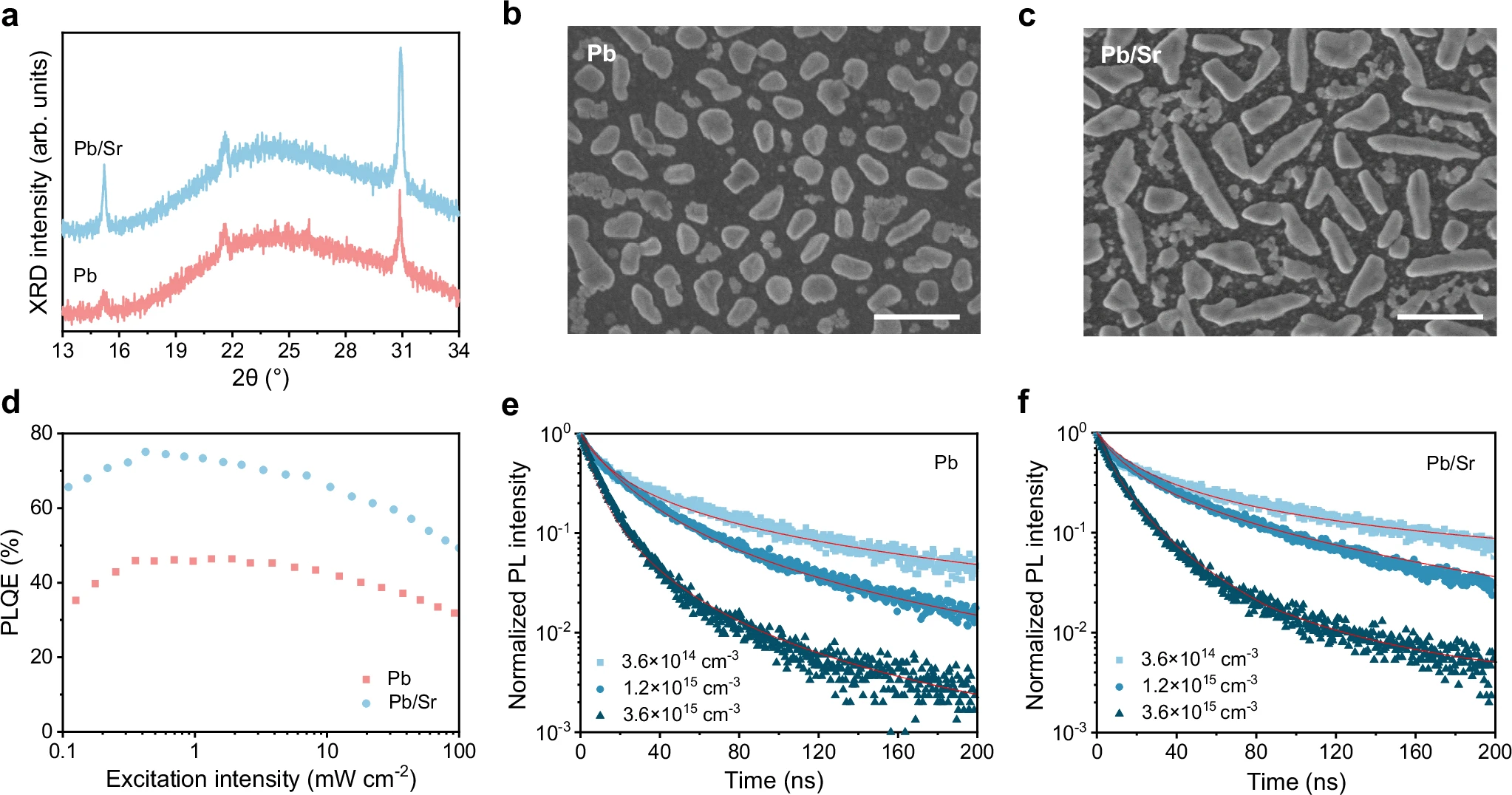
adminRecent advancements in all-site alloyed perovskites have significantly improved the performance of blue perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs), addressing key challenges such as bandgap tuning, halide segregation, and defect-related losses. By simultaneously modifying the A-site (cations), B-site (metal ions), and X-site (halides), researchers have achieved stable, efficient, and bright blue emission. Notable breakthroughs include EQE >10% for sky-blue PeLEDs (~470 nm) and improved operational stability. Further optimization of compositional engineering and dimensional confinement (e.g., quasi-2D phases) may enable deep-blue emission (<450 nm) and lead-free alternatives, paving the way for commercial applications in displays and lighting.
Link:All-site alloyed perovskite for efficient and bright blue light-emitting diodes | Nature Communications